
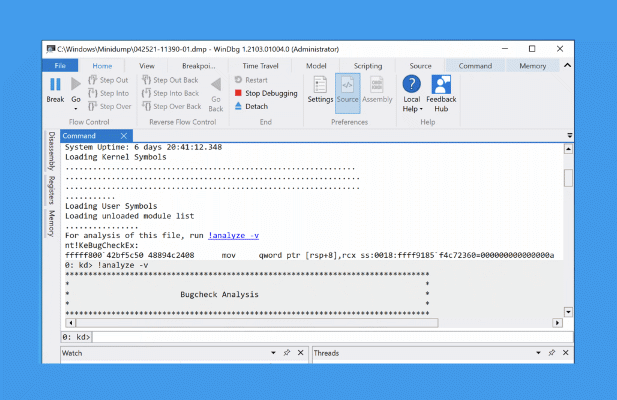
These dump files exist to provide you with information about the cause of the system crash. (none): Windows won’t create memory dumps when it crashes. The page file must be large enough to contain the memory data. Microsoft says that, when the page file is set to a system-managed size and the computer is configured for automatic memory dumps, “Windows sets the size of the paging file large enough to ensure that a kernel memory dump can be captured most of the time.” As Microsoft points out, crash dumps are an important consideration when deciding what size the page file should be. RELATED: How Big Should Your Page File or Swap Partition Be?Īutomatic memory dump: This is the default option, and it contains the exact same information as a kernel memory dump. It can be helpful for identifying the error, but offers less detailed debugging information than a kernel memory dump.
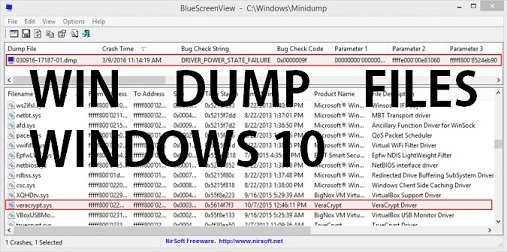
It contains very little information - the blue-screen information, a list of loaded drivers, process information, and a bit of kernel information. Small memory dump (256 kb): A small memory dump is the smallest type of memory dump. It is significantly smaller than the Complete Memory Dump, but it only omits those portions of memory that are unlikely to have been involved in the crash.” It only includes memory allocated to the Windows kernel and hardware abstraction level (HAL), as well as memory allocated to kernel-mode drivers and other kernel-mode programs.įor most purposes, this crash dump is the most useful. “This dump file will not include unallocated memory, or any memory allocated to user-mode applications. Microsoft says it will typically be about one-third the size of the physical memory installed on the system. Kernel memory dump: A kernel memory dump will be much smaller than a complete memory dump. Crashes are usually caused by code running in kernel-mode, so the complete information including each program’s memory is rarely useful - a kernel memory dump will usually be sufficient even for a developer. So, if you have 16 GB of RAM and Windows is using 8 GB of it at the time of the system crash, the memory dump will be 8 GB in size. This contains a copy of all the data used by Windows in physical memory. Click Advanced system settings in the sidebar, click the Advanced tab, and click Settings under Startup and recovery.īy default, the setting under Write debugging information is set to “Automatic memory dump.” Here’s what each type of memory dump actually is:Ĭomplete memory dump: A complete memory dump is the largest type of possible memory dump. You can access this setting by opening the Control Panel, clicking System and Security, and clicking System. Windows can create several different types of memory dumps. RELATED: Everything You Need To Know About the Blue Screen of Death


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
